Introduction#
In today’s digital world, data security is more critical than ever. Whether you’re shopping online or communicating confidential information, encryption plays a vital role in keeping your data safe. One of the most widely used encryption algorithms is AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), known for its speed and security.
In this post, we’ll explore what AES is, why it matters, and how to implement it using C code.
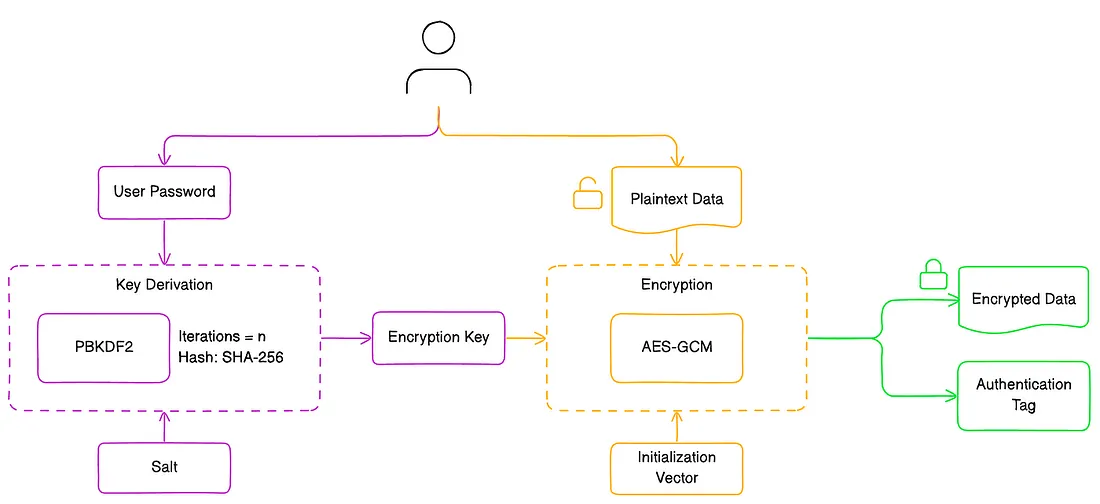
What Is AES Encryption?#
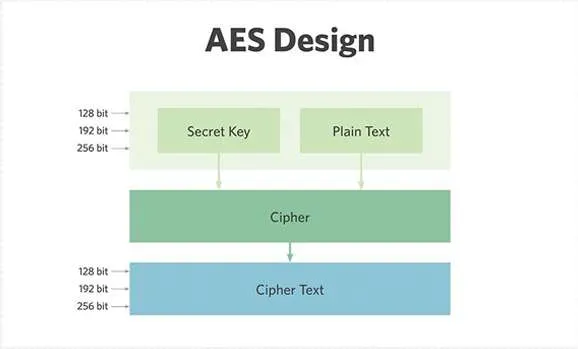
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm, which means the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. Developed by Vincent Rijmen and Joan Daemen, AES was adopted by the U.S. government as the encryption standard in 2001 and remains a cornerstone of modern cryptographic security.
- AES supports three key lengths:
128, 192, and 256 bits, offering varying levels of security
Simple AES Encryption in C (Pseudo-Implementation)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <openssl/aes.h>
void encryptAES(const unsigned char *plaintext, const unsigned char *key, unsigned char *ciphertext) {
AES_KEY encryptKey;
AES_set_encrypt_key(key, 128, &encryptKey);
AES_encrypt(plaintext, ciphertext, &encryptKey);
}
int main() {
unsigned char key[16] = "mysecretkey12345";
unsigned char plaintext[16] = "HelloAESWorld!!";
unsigned char ciphertext[16];
encryptAES(plaintext, key, ciphertext);
printf("Encrypted Ciphertext: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
printf("%02x ", ciphertext[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Why Is AES Important?#
AES has become the encryption standard for countless applications due to its:
Efficiency:AES is fast, even on resource-constrained devices.Security:Resistant to all known practical attacks, including brute force.Versatility:Used for securing everything from file storage to communication protocols.
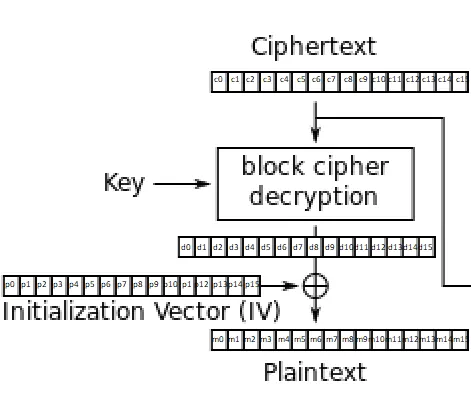
AES Decryption Example in C#
void decryptAES(const unsigned char *ciphertext, const unsigned char *key, unsigned char *decryptedText) {
AES_KEY decryptKey;
AES_set_decrypt_key(key, 128, &decryptKey);
AES_decrypt(ciphertext, decryptedText, &decryptKey);
}
int main() {
unsigned char key[16] = "mysecretkey12345";
unsigned char ciphertext[16] = {0xe2, 0x91, 0x3f, 0x5b, 0xa1, 0x71, 0xf4, 0x2e, 0x6d, 0x4e, 0xae, 0xfb, 0x72, 0xcd, 0xa5, 0x6a};
unsigned char decryptedText[16];
decryptAES(ciphertext, key, decryptedText);
printf("Decrypted Text: %s\n", decryptedText);
return 0;
}
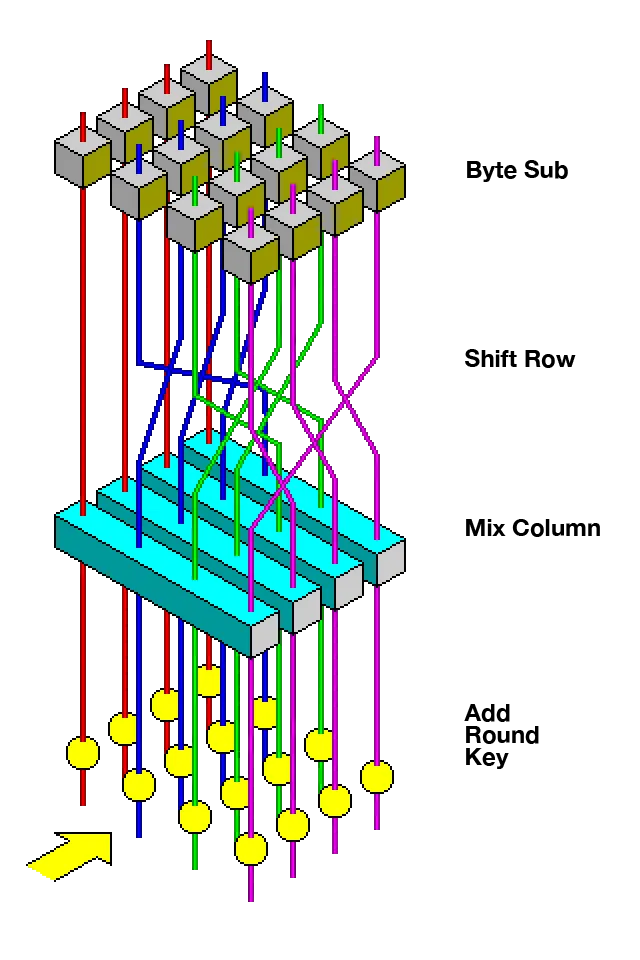
How AES Works:#
AES operates on blocks of 128 bits and transforms plaintext into ciphertext through multiple rounds of processing. Each round involves:
SubBytes:Non-linear substitution of bytes using an S-Box.ShiftRows:Row shifting for diffusion.MixColumns:Mixing bytes for further diffusion (except in the final round).AddRoundKey:XOR operation between the block and a round key.
Key Schedule in AES#
(Round Key Generation)
#include <openssl/aes.h>
void displayRoundKey(const unsigned char *key) {
for (int i = 0; i < AES_BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
printf("%02x ", key[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
unsigned char key[16] = "testkeyforround";
unsigned char roundKey[AES_BLOCK_SIZE];
AES_KEY aesKey;
AES_set_encrypt_key(key, 128, &aesKey);
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
printf("Round %d Key: ", i);
displayRoundKey((unsigned char *)&aesKey.rd_key[i * 4]);
}
return 0;
}
Applications of AES#
AES is widely used across industries and applications, including:
Secure Communications:Protecting data over TLS and VPNsFile Encryption:Keeping sensitive information secure in storageWireless Security:Protecting Wi-Fi networks through WPA2Cryptocurrencies:Securing blockchain transactions
The Future of AES Encryption#
While AES remains one of the most secure algorithms available, emerging technologies like quantum computing present potential threats. Post-quantum cryptography aims to develop encryption algorithms resistant to quantum attacks.
Final Thoughts#
AES is a critical tool in modern cybersecurity. Understanding how it works and implementing it in code is essential for anyone interested in cryptography or secure software development.





